TECHNICAL BLOG
Direct Quantum Compute-as-a-Service with OQC and Equinix

Atsushi Sugiura
HEAD OF COMMERCIAL, APAC & COUNTRY MANAGER JAPAN
Atsushi is the Head of Commercial, APAC and the Japan Country Manager at OQC. With an impressive track record spanning over 30 years, Atsushi possesses extensive expertise in the IT industry, garnered through his work in Japan and internationally. His career has primarily focused on High-Performance Computing and Enterprise systems, with notable positions held at renowned Japanese and global enterprises such as Itochu Corporation, Sun Microsystems, Silicon Graphics International (SGI), Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), and Advanced Micro Devices (AMD).
The technological world is continuously developing and quantum computing is an increasingly desired asset for businesses, with McKinsey estimating that by 2035, quantum computing could create 622 billion USD in value for the finance sector alone. Traditionally, quantum computers have been hosted in research environments or vendor facilities which prompted considerations of data security, privacy, and reliability. Computers being hosted in these facilities require the action of standard access policies and procedures, which often poses near insurmountable challenges to data and network security professionals; particularly when most corporate and institutional IT policies significantly limit the exposure to open networks, such as the public internet.
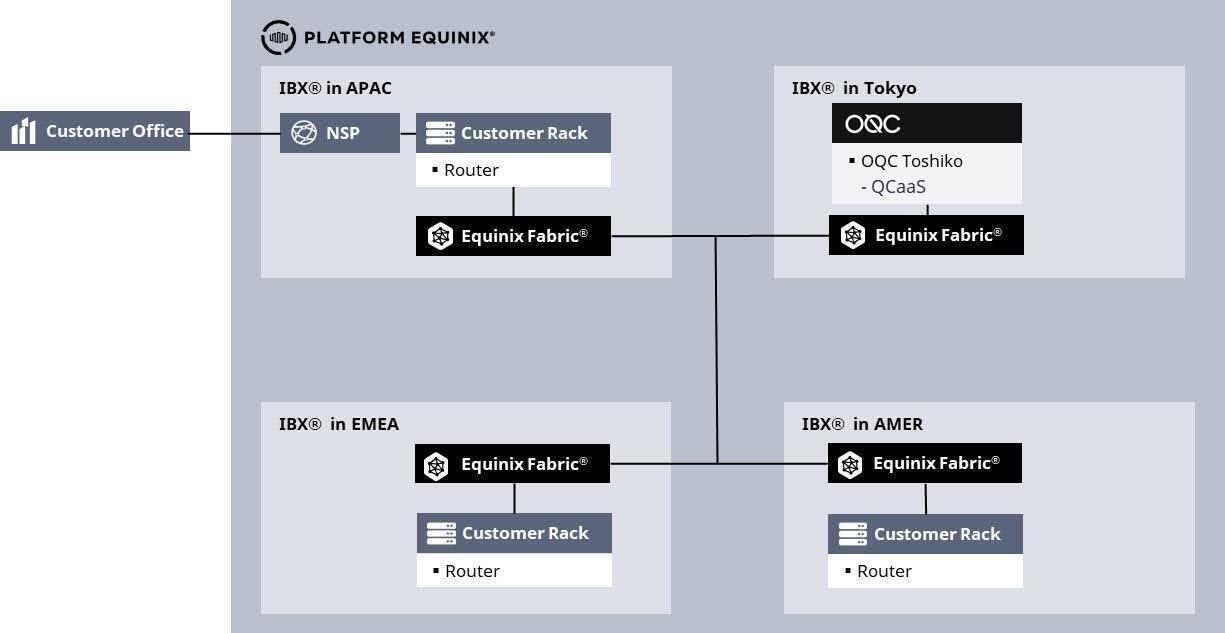
To mitigate these issues, OQC have partnered with Equinix to integrate their latest 32-qubit device into Equinix’s TY11 Tokyo International Business Exchange™ (IBX®) data centre. This integration has created a secure access option via Equinix Fabric for organisations looking to experiment with quantum compute and is a world-first achievement by OQC.
A new technology for new problems
Quantum computers have evolved into an enterprise-ready ‘out-of-lab’ stage with OQC being the first to integrate a quantum computer into a colocation data centre to accelerate the technology and ecosystem development.
The development of quantum computing is growing in importance for two key reasons;
- First, the demand for computational power and capability is increasing, exemplified by the emergence of generative AI and the advancement of GPU-powered high-performance computing. Moore’s Law, the principle guiding the age of exponential progress in classical computing, is reaching its natural limits; and with its end nigh, we must now begin the search for usable and scalable alternative technologies. This call for such alternative technologies is becoming louder as electric power becomes harder to source, unsustainable to use indiscriminately, and power efficiency becomes a priority around the globe.
- Second, as society becomes increasingly digitised and reliant on electronic communications, the ever-increasing need for robust cybersecurity and stronger encryption algorithms requires innovative solutions that could move beyond the ability of current computational platforms to offer.
With these points in mind, we believe now is the time to accelerate the development of quantum computing by making quantum systems broadly available to more stakeholders to generate a more sustainable, capable, and secure computing paradigm. This is achieved by moving quantum computing out of lab environments and into a more accessible environment. OQC have proved increasing accessibility, quality, and security can be done simultaneously by deploying a quantum computer into Equinix’s vast industry ecosystem and bringing Quantum Computing-as-a-Service (QCaaS) to their users with secure, private, on-demand connection.
OQC demonstrated this by deploying OQC Toshiko, their latest quantum computer, at Equinix in Tokyo, Japan. OQC Toshiko, in the Equinix TY11 IBX® data centre, has shown improved operational quality, such as better computation results, over OQC Lucy, which was in the OQC lab, and OQC Toshiko has shown unheard of resiliency; having remained coherent and operational even during a magnitude 5 earthquake.
Transitioning quantum computing from a R&D lab to a highly accessible commercial environment requires overcoming unique challenges inherent to quantum devices. Quantum devices are extremely sensitive to environmental noise such as vibration, electromagnetic, acoustic, and others found in data centres (in fact, it is this sensitivity that makes quantum sensors and detectors so effective). Classical computers are tolerant of such noises; however, those same noises can be obstacles for quantum computers. OQC’s unique Coaxmon technology gives a reduction in drive coupling between qubits, which in turn supports its capability to resist and continue to operate under such noises.
To find out more about OQC’s world first integration of a quantum computer into a colocation data centre, download our free whitepaper here.

Equinix Fabric: easy and secure access to quantum compute
Built upon a hybrid and multicloud foundation, Equinix’s global digital infrastructure platform brings quantum directly to where the data resides, along with providing high speed connectivity to an extensive ecosystem of providers and partners. This enables enterprises to maintain ownership over their data while complying with data sovereignty and regulatory requirements. Equinix also offers access to dedicated and managed infrastructure, simplifying the development, deployment, and management of applications while ensuring predictable costs and high performance.
Equinix Fabric, a software-defined interconnection service that enables dynamic and secure connections between physical and virtual infrastructures across a global network, enables its customers to build “as-a-service” solutions. Equinix Fabric is a key enabler for OQC’s customers to access OQC Toshiko. Customers can achieve direct and private connectivity to OQC’s quantum computing services from any location within Equinix’s global data centres. This capability allows for easy, efficient, and private access to quantum computing, ensuring seamless integration with existing computing and data storage infrastructure. The strength of Equinix Fabric lies in its ability to deliver secure, fast, reliable, and scalable interconnections.
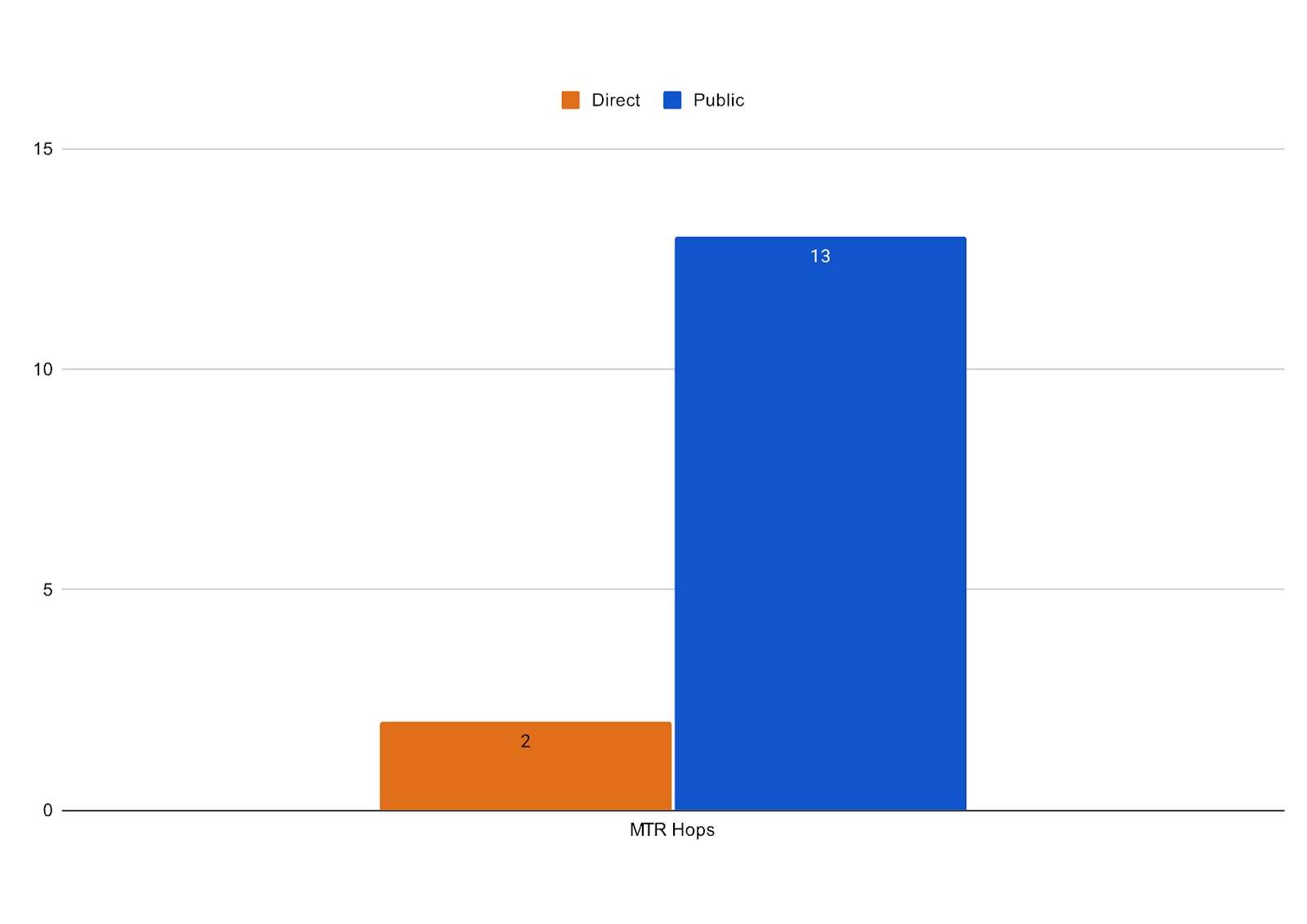
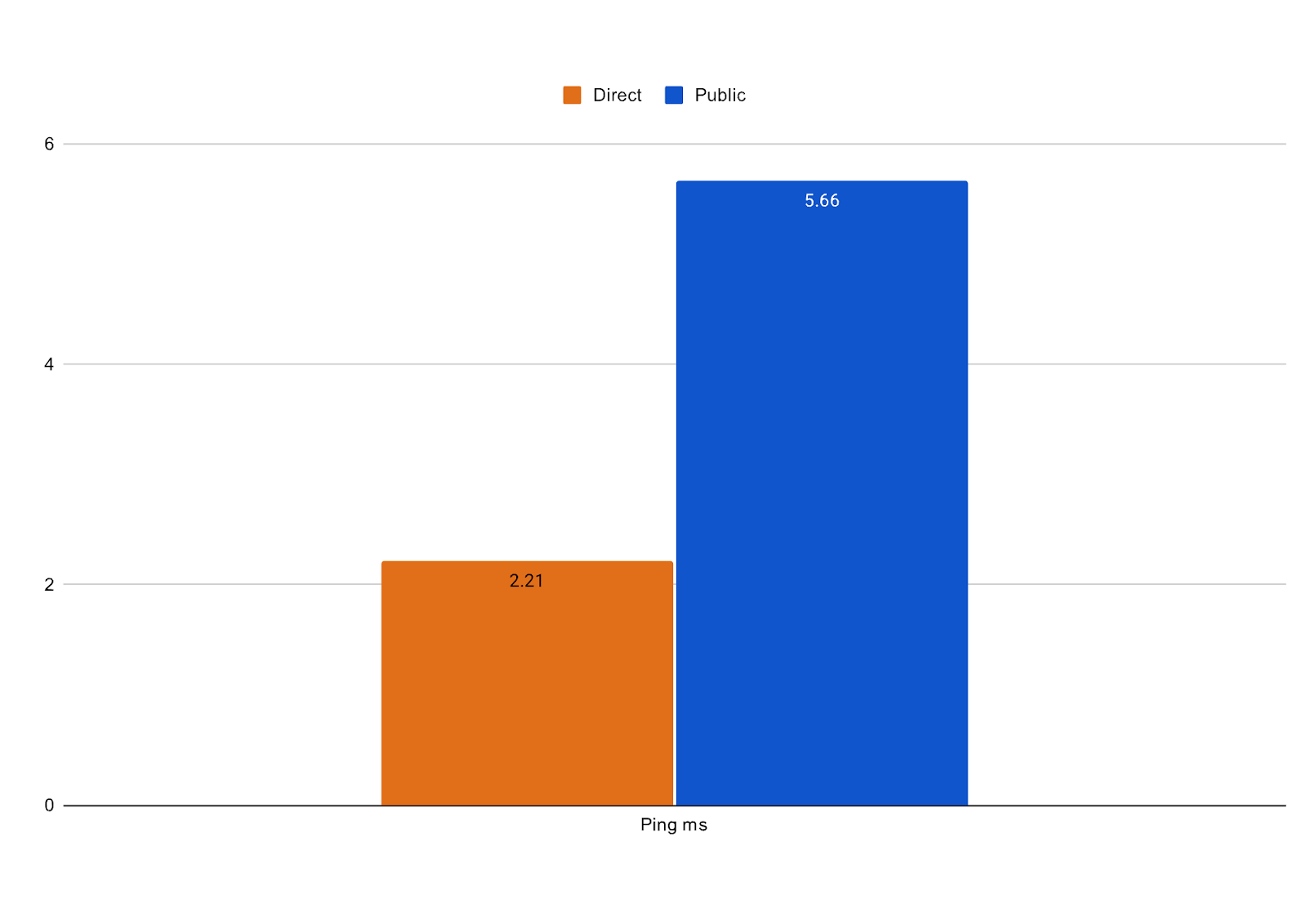
Considering latency
High latency can slow down even the fastest Internet connection and cause critical services to be slow. Applications that are particularly data-intensive are most affected by latency issues, however, Direct QCaaS servers enabled by Equinix Fabrics low-latency connectivity shows reduction in key network metrics for such applications. Below shows a clear advantage of using the Equinix Fabric over general internet (test conducted within Tokyo Metro Area).
By avoiding unpredictable public internet routing, customers can benefit from lower network latency and better reliability.
Equinix Fabric differentiates itself from general Internet access by offering a more secure, reliable, and high-performance connectivity solution. While Internet access is typically shared and subject to potential congestion and security risks, Equinix Fabric provides dedicated and private connections within Equinix’s global data centres. This ensures faster and more consistent data transfer, minimum latency, and improved reliability.
Addressing IT policies
With advanced technologies in a highly digitised world, it has become easier for malicious actors to attack and exploit security vulnerabilities. These attacks can create a significant impact on corporations and government bodies. The importance of security and information management could not be more important in this digital age.
The global financial sector
In major countries within the financial sector, there have been updates and introductions of new policies regarding cybersecurity. In 2023, the US Securities and Exchange Commission adopted new regulations concerning cybersecurity risk management, strategy, governance, and incident disclosure.*1 Also, the FBI’s 2023 Internet Crime Report highlighted a substantial rise in investment fraud, with losses reaching $4.57 billion – a 38% increase from the previous year.*2 Furthermore, in 2024, Singapore revised its cybersecurity law, strengthening regulations for critical infrastructure operators, including financial institutions, where they are faced with reinforced obligations for inspection orders from the Cyber Security Agency.*3
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe*4
The need for robust information security has been significantly reinforced by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe. GDPR mandates stringent data protection measures, requiring organisations to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of personal data. This regulation has heightened the importance of cybersecurity, as companies must implement comprehensive strategies to protect sensitive information from unauthorised access and breaches. The emphasis on compliance with GDPR drives organisations to adopt advanced security protocols to safeguard data privacy and integrity, making cybersecurity an essential component of modern information management practices.
Manufacturing, industrial, material sectors*5
In the manufacturing, industrial, and material sectors, the integration of IoT and digital transformation technologies is revolutionising operations and information management. Manufacturing plants are increasingly adopting IoT devices to monitor and optimise production processes in real-time, leading to enhanced efficiency and reduced downtime. Digital transformation extends to supply chain management, where advanced data analytics and automation streamline operations, improve delivery accuracy, and reduce costs. The digitalisation driven by these technologies requires robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with stringent IT policies. This emphasis on secure information management is crucial in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of digitally transformed manufacturing environments.
IT policies and their implementation
IT policies in organisations are increasingly restrictive regarding the exposure of data to an open network. By enabling access to quantum computing and other classical infrastructure through Equinix Fabric’s private network, such IT policies are satisfied and traffic remains secure. Also, managing data locations from a data sovereignty standpoint is a fundamental part of IT policy today. Equinix’s 260+ data centre facilities in each region around the globe help organisations effectively locate and manage their data.
By seamlessly integrating quantum technology into existing industrial infrastructures, OQC empowers companies to drive innovation and maintain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market. The commitment to data security is paramount, with OQC’s solutions offering robust protection for personal and organisational data.
We invite those who are responsible for IT policies, including cybersecurity, compliance and information management, to explore the transformative potential of Quantum Compute-as-a-Service (QCaaS). Contact us today to learn more about how our secure and advanced quantum computing solutions can revolutionise your business operations and ensure compliance with the highest IT security standards. Take the first step towards a future of enhanced security and unparalleled computational power with OQC and Equinix.
About OQC
OQC is Europe’s first Quantum Computing-as-a-Service company, offering a quantum computer, OQC Toshiko, that seamlessly integrates into digital infrastructures and customer workflows. OQC is currently the only enterprise-ready quantum computing company, designing systems for deployment in commercial data centres such as those provided by Equinix.
About Equinix
Equinix (Nasdaq: EQIX) is the world’s digital infrastructure company®. Digital leaders harness Equinix’s trusted platform to bring together and interconnect foundational infrastructure at software speed. Equinix enables organizations to access all the right places, partners and possibilities to scale with agility, speed the launch of digital services, deliver world-class experiences and multiply their value, while supporting their sustainability goals.
References:
*1 SEC.gov | SEC Adopts Rules on Cybersecurity Risk Management, Strategy, Governance, and Incident Disclosure by Public Companies
*2 FBI Releases Internet Crime Report — FBI
*3 CSA First Reading of the Cybersecurity (Amendment) Bill
*4 GDPR at a glance: PwC
*5 Cybersecurity for Smart Factories in the Manufacturing Industry | Deloitte US
Join our newsletter for more articles like this
By clicking ‘sign up’ you’re confirming that you agree with our Terms & Conditions